This is the multi-page printable view of this section.
Click here to print.
Return to the regular view of this page.
Deck
Shows what jobs are running or have recently run in prow
Running Deck locally
Deck can be run locally by executing ./cmd/deck/runlocal. The scripts starts Deck via
Bazel using:
- pre-generated data (extracted from a running Prow instance)
- the local
config.yaml
- the local static files, template files and lenses
Open your browser and go to: http://localhost:8080
Debugging via Intellij / VSCode
This section describes how to debug Deck locally by running it inside
VSCode or Intellij.
# Prepare assets
make build-tarball PROW_IMAGE=cmd/deck
mkdir -p /tmp/deck
tar -xvf ./_bin/deck.tar -C /tmp/deck
cd /tmp/deck
# Expand all layers
for tar in *.tar.gz; do tar -xvf $tar; done
# Start Deck via go or in your IDE with the following arguments:
--config-path=./config/prow/config.yaml
--job-config-path=./config/jobs
--hook-url=http://prow.k8s.io
--spyglass
--template-files-location=/tmp/deck/var/run/ko/template
--static-files-location=/tmp/deck/var/run/ko/static
--spyglass-files-location=/tmp/deck/var/run/ko/lenses
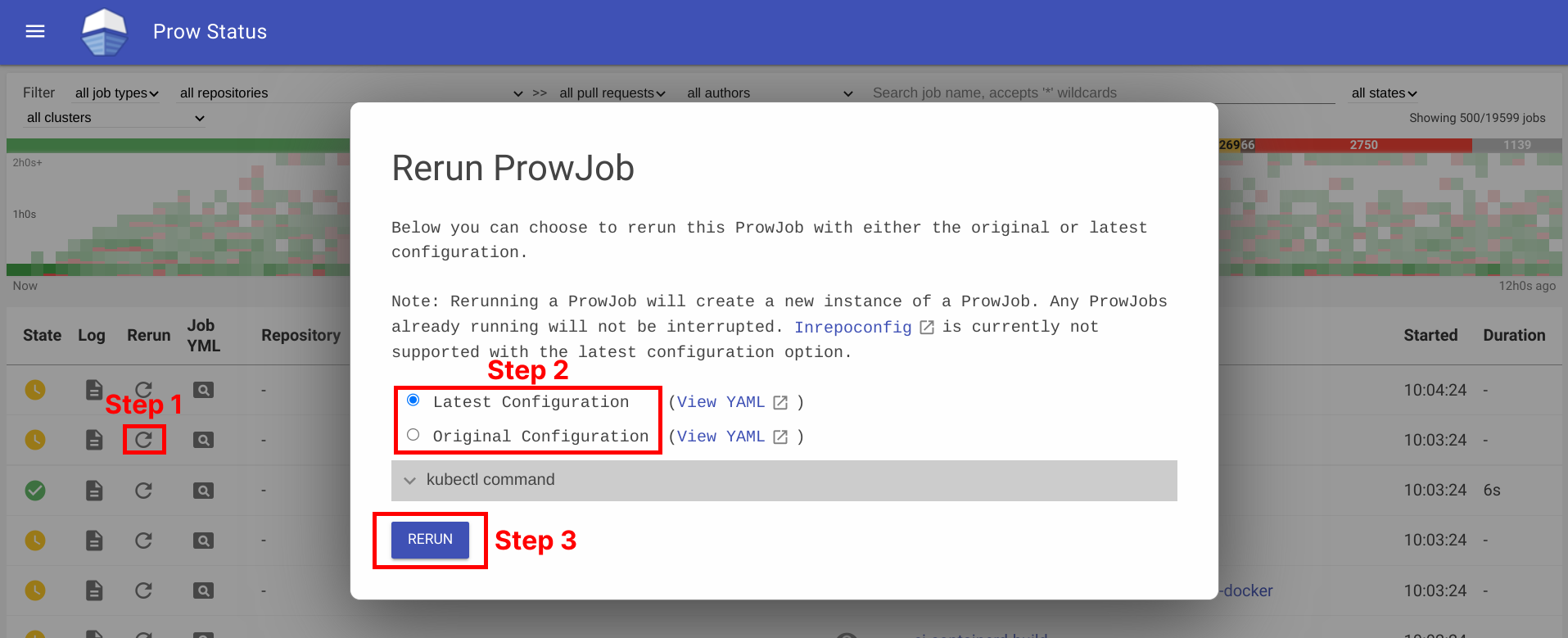
Rerun Prow Job via Prow UI
Rerun prow job can be done by visiting prow UI, locate prow job and rerun job by clicking on the ↻ button, selecting a configuration option, and then clicking Rerun button. For prow on github, the permission is controlled by github membership, and configured as part of deck configuration, see rerun_auth_configs for k8s prow.
See example below:
Rerunning can also be done on Spyglass:
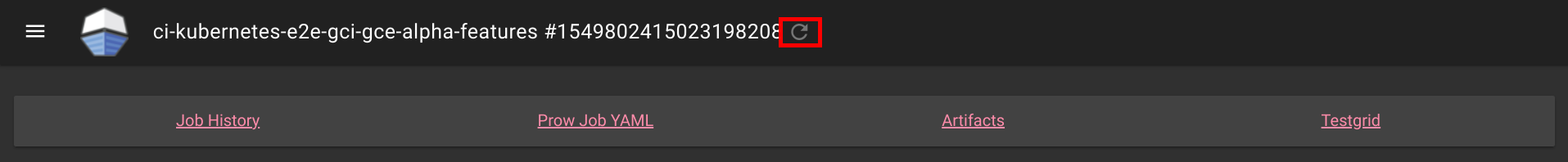
This is also available for non github prow if the frontend is secured and allow_anyone is set to true for the job.
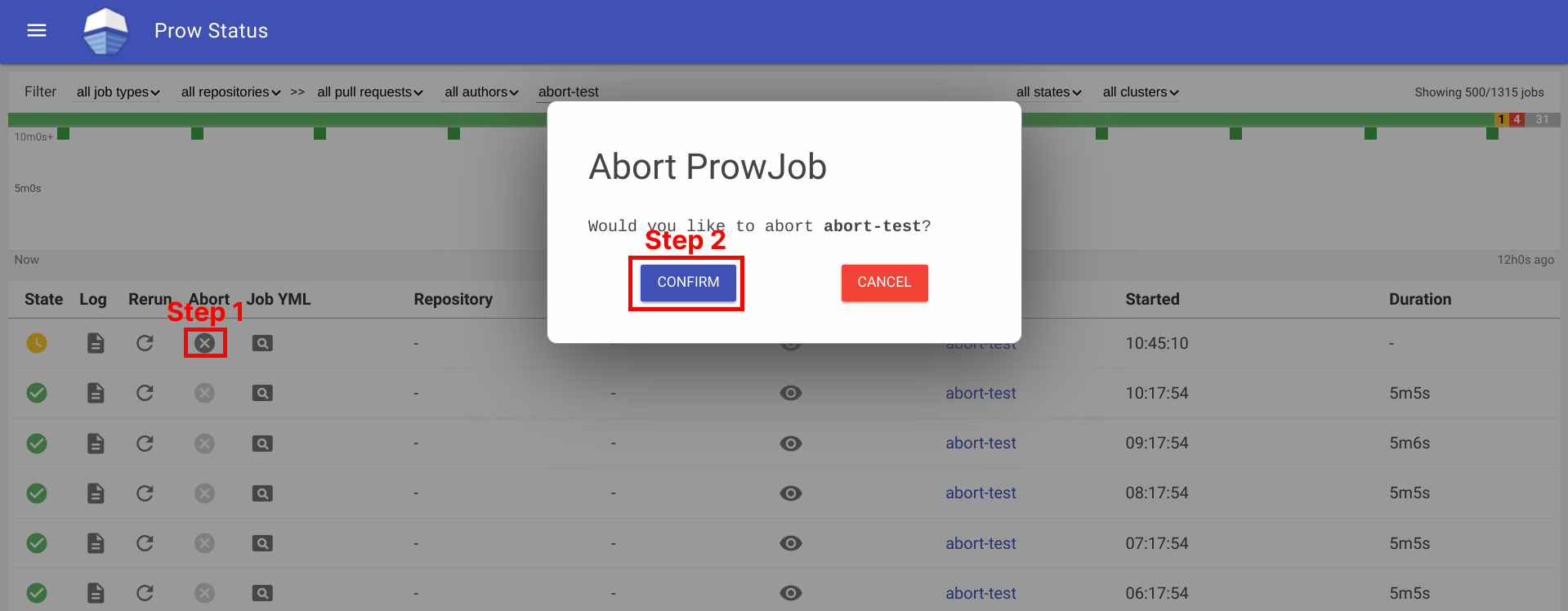
Abort Prow Job via Prow UI
Aborting a prow job can be done by visiting the prow UI, locate the prow job and abort the job by clicking on the ✕ button, and then clicking Confirm button. For prow on github, the permission is controlled by github membership, and configured as part of deck configuration, see rerun_auth_configs for k8s prow. Note, the abort functionality uses the same field as rerun for permissions.
See example below:
Aborting can also be done on Spyglass:

This is also available for non github prow if the frontend is secured and allow_anyone is set to true for the job.
1 - How to setup GitHub Oauth
This document helps configure GitHub Oauth, which is required for PR Status
and for the rerun button on Prow Status.
If OAuth is configured, Prow will perform GitHub actions on behalf of the authenticated users.
This is necessary to fetch information about pull requests for the PR Status page and to
authenticate users when checking if they have permission to rerun jobs via the rerun button on Prow Status.
Set up secrets
The following steps will show you how to set up an OAuth app.
-
Create your GitHub Oauth application
https://developer.github.com/apps/building-oauth-apps/creating-an-oauth-app/
Make sure to create a GitHub Oauth App and not a regular GitHub App.
The callback url should be:
<PROW_BASE_URL>/github-login/redirect
-
Create a secret file for GitHub OAuth that has the following content. The information can be found in the GitHub OAuth developer settings:
client_id: <APP_CLIENT_ID>
client_secret: <APP_CLIENT_SECRET>
redirect_url: <PROW_BASE_URL>/github-login/redirect
final_redirect_url: <PROW_BASE_URL>/pr
If Prow is expected to work with private repositories, add
-
Create another secret file for the cookie store. This cookie secret will also be used for CSRF protection.
The file should contain a random 32-byte length base64 key. For example, you can use openssl to generate the key
openssl rand -out cookie.txt -base64 32
-
Use kubectl, which should already point to your Prow cluster, to create secrets using the command:
kubectl create secret generic github-oauth-config --from-file=secret=<PATH_TO_YOUR_GITHUB_SECRET>
kubectl create secret generic cookie --from-file=secret=<PATH_TO_YOUR_COOKIE_KEY_SECRET>
-
To use the secrets, you can either:
-
Mount secrets to your deck volume:
Open test-infra/config/prow/cluster/deck_deployment.yaml.
Under volumes token, add:
- name: oauth-config
secret:
secretName: github-oauth-config
- name: cookie-secret
secret:
secretName: cookie
Under volumeMounts token, add:
- name: oauth-config
mountPath: /etc/githuboauth
readOnly: true
- name: cookie-secret
mountPath: /etc/cookie
readOnly: true
-
Add the following flags to deck:
- --github-oauth-config-file=/etc/githuboauth/secret
- --oauth-url=/github-login
- --cookie-secret=/etc/cookie/secret
Note that the --oauth-url should eventually be changed to a boolean as described
in #13804.
-
You can also set your own path to the cookie secret using the --cookie-secret flag.
-
To prevent deck from making mutating GitHub API calls, pass in the --dry-run flag.
Using A GitHub bot
The rerun button can be configured so that certain GitHub teams are allowed to trigger certain jobs
from the frontend. In order to make API calls to determine whether a user is on a given team, deck needs
to use the access token of an org member.
If not, you can create a new GitHub account, make it an org member, and set up a personal access token
here.
Then create the access token secret:
kubectl create secret generic oauth-token --from-file=secret=<PATH_TO_ACCESS_TOKEN>
Add the following to volumes and volumeMounts:
volumeMounts:
- name: oauth-token
mountPath: /etc/github
readOnly: true
volumes:
- name: oauth-token
secret:
secretName: oauth-token
Pass the file path to deck as a flag:
--github-token-path=/etc/github/oauth
You can optionally use ghproxy to reduce token usage.
Run PR Status endpoint locally
Firstly, you will need a GitHub OAuth app. Please visit step 1 - 3 above.
When testing locally, pass the path to your secrets to deck using the --github-oauth-config-file and --cookie-secret flags.
Run the command:
go build . && ./deck --config-path=../../../config/prow/config.yaml --github-oauth-config-file=<PATH_TO_YOUR_GITHUB_OAUTH_SECRET> --cookie-secret=<PATH_TO_YOUR_COOKIE_SECRET> --oauth-url=/pr
Using a test cluster
If hosting your test instance on http instead of https, you will need to use the --allow-insecure flag in deck.
2 - CSRF attacks
In Deck, we make a number of POST requests that require user authentication. These requests are susceptible
to cross site request forgery (CSRF) attacks,
in which a malicious actor tricks an already authenticated user into submitting a form to one of these endpoints
and performing one of these protected actions on their behalf.
Protection
If --cookie-secret is 32 or more bytes long, CSRF protection is automatically enabled.
If --rerun-creates-job is specified, CSRF protection is required, and accordingly,
--cookie-secret must be 32 bytes long.
We protect against CSRF attacks using the gorilla CSRF library, implemented
in #13323. Broadly, this protection works by ensuring that
any POST request originates from our site, rather than from an outside link.
We do so by requiring that every POST request made to Deck includes a secret token either in the request header
or in the form itself as a hidden input.
We cryptographically generate the CSRF token using the --cookie-secret and a user session value and
include it as a header in every POST request made from Deck.
If you are adding a new POST request, you must include the CSRF token as described in the gorilla
documentation.
The gorilla library expects a 32-byte CSRF token. If --cookie-secret is sufficiently long,
direct job reruns will be enabled via the /rerun endpoint. Otherwise, if --cookie-secret is less
than 32 bytes and --rerun-creates-job is enabled, Deck will refuse to start. Longer values will
work but should be truncated.
By default, gorilla CSRF requires that all POST requests are made over HTTPS. If developing locally
over HTTP, you must specify --allow-insecure to Deck, which will configure both gorilla CSRF
and GitHub oauth to allow HTTP requests.
CSRF can also be executed by tricking a user into making a state-mutating GET request. All
state-mutating requests must therefore be POST requests, as gorilla CSRF does not secure GET
requests.



